We need a lot more vitamin D than the official recommendations
 Lack of vitamin D is linked to an increased risk of virus infections, respiratory diseases, cardiovascular diseases, dementia, cancer, and osteoporosis. However, the official recommendations for vitamin D intake are way too low, according to two new studies that were presented at the American Heart Association’s Scientific Sessions in Philadelphia in 2023. In addition, a German study of athletes has shown that it is better to take individually tailored vitamin D supplements to optimize blood levels of the nutrient instead of using a “one-size-fits-all” solution.
Lack of vitamin D is linked to an increased risk of virus infections, respiratory diseases, cardiovascular diseases, dementia, cancer, and osteoporosis. However, the official recommendations for vitamin D intake are way too low, according to two new studies that were presented at the American Heart Association’s Scientific Sessions in Philadelphia in 2023. In addition, a German study of athletes has shown that it is better to take individually tailored vitamin D supplements to optimize blood levels of the nutrient instead of using a “one-size-fits-all” solution.
Read more about why we need much more vitamin D than officially recommended
- Created on .


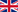
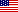



 The number of older people is increasing rapidly, which means more and more people suffer from different types of dementia.
The number of older people is increasing rapidly, which means more and more people suffer from different types of dementia. 
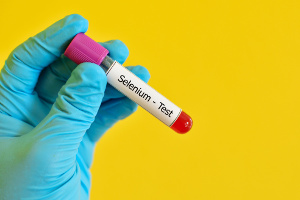 Cholesterol is an essential compound with many different functions. However, it can also turn into a potentially dangerous substance if it oxidizes and is embedded in the blood vessel walls. This oxidative process is what eventually leads to atherosclerosis. The trace element selenium protects against atherosclerosis because of its antioxidant properties and because of other mechanisms, according to a review article published in Biomedicine. This is highly relevant in our part of the world where cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death, and where
Cholesterol is an essential compound with many different functions. However, it can also turn into a potentially dangerous substance if it oxidizes and is embedded in the blood vessel walls. This oxidative process is what eventually leads to atherosclerosis. The trace element selenium protects against atherosclerosis because of its antioxidant properties and because of other mechanisms, according to a review article published in Biomedicine. This is highly relevant in our part of the world where cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death, and where 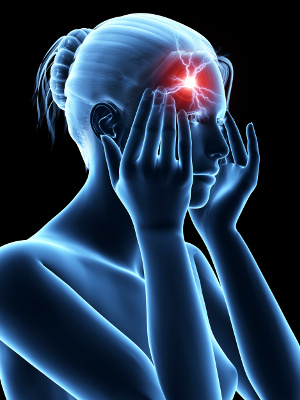 Migraine headaches, a problem that affects far more women than men, is one of the diseases that costs most sick days, and there is no medical treatment that can cure the underlying cause. What we eat appears to play a major role, which is because foods such as matured cheese, chocolate, caffeinated beverages, red wine, and monosodium glutamate (MSG) can trigger migraines and headaches. Also, eating an unbalanced diet that is low in specific nutrients such as magnesium, B vitamins, and Q10 can disrupt certain metabolic processes, thereby setting off an attack. This was seen in a new study that is published in Frontiers in Nutrition.
Migraine headaches, a problem that affects far more women than men, is one of the diseases that costs most sick days, and there is no medical treatment that can cure the underlying cause. What we eat appears to play a major role, which is because foods such as matured cheese, chocolate, caffeinated beverages, red wine, and monosodium glutamate (MSG) can trigger migraines and headaches. Also, eating an unbalanced diet that is low in specific nutrients such as magnesium, B vitamins, and Q10 can disrupt certain metabolic processes, thereby setting off an attack. This was seen in a new study that is published in Frontiers in Nutrition.


 Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) that is linked to overweight and type 2 diabetes may eventually cause critical liver inflammation, liver fibrosis, and liver cancer. The diet plays a major role, and scientists from Oregon State University have observed that the
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) that is linked to overweight and type 2 diabetes may eventually cause critical liver inflammation, liver fibrosis, and liver cancer. The diet plays a major role, and scientists from Oregon State University have observed that the