Lack of vitamin C increases the risk of eye disease in pregnant diabetics
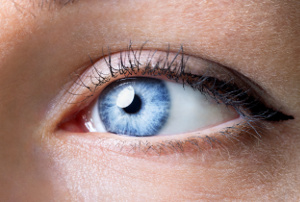 It is commonly known that pregnant diabetics have an increased risk of developing an eye disease called diabetic retinopathy. The diet plays a major role and it appears that a vitamin C deficiency increases the risk, according to a Danish study of pregnant type 1 diabetics that is published in the journal Antioxidants. The authors also mention that vitamin C is a vital antioxidant that protects cells and tissues against oxidative stress caused by free radicals.
It is commonly known that pregnant diabetics have an increased risk of developing an eye disease called diabetic retinopathy. The diet plays a major role and it appears that a vitamin C deficiency increases the risk, according to a Danish study of pregnant type 1 diabetics that is published in the journal Antioxidants. The authors also mention that vitamin C is a vital antioxidant that protects cells and tissues against oxidative stress caused by free radicals.
Read more about how lack of vitamin C increases the risk of eye disease in pregnant diabetics
- Created on .





 Poor sperm quality, which is a bit of a taboo, is one of the main causes of involuntary infertility. Evidence suggests that Western diets can impair sperm quality, whereas the Mediterranean diet does the opposite. Vegan diets are somewhat controversial, according to a review article published in International Journal of Molecular Sciences. Previous research has shown that supplementation with selenium, zinc, fish oil, and coenzyme Q10 can improve sperm cell quality.
Poor sperm quality, which is a bit of a taboo, is one of the main causes of involuntary infertility. Evidence suggests that Western diets can impair sperm quality, whereas the Mediterranean diet does the opposite. Vegan diets are somewhat controversial, according to a review article published in International Journal of Molecular Sciences. Previous research has shown that supplementation with selenium, zinc, fish oil, and coenzyme Q10 can improve sperm cell quality. Most people have experienced a normal headache, while migraines are far more complex. Although the pain can be caused by a number of factors, essential nutrients such as B vitamins, vitamin D, magnesium, fish oil, and coenzyme Q10 may play a vital role according to a review article that is published in Current Pain and Headache Reports. The authors describe how certain nutrients affect underlying mechanisms that may prevent or mitigate different types of headaches.
Most people have experienced a normal headache, while migraines are far more complex. Although the pain can be caused by a number of factors, essential nutrients such as B vitamins, vitamin D, magnesium, fish oil, and coenzyme Q10 may play a vital role according to a review article that is published in Current Pain and Headache Reports. The authors describe how certain nutrients affect underlying mechanisms that may prevent or mitigate different types of headaches.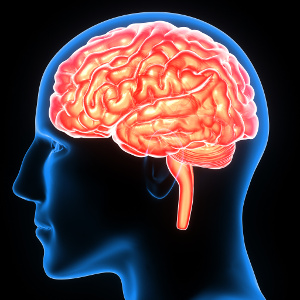 Fish oil contains EPA and DHA, two omega-3 fatty acids with a number of different functions in the brain and nervous system. It appears that middle-aged people who consume more oily fish or who take fish oil supplements have improvements in their brain structure and cognitive skills. This was shown in a study that is published in Neurology. The study results are quite interesting because cognitive decline and dementia are increasing problems that affect millions of people worldwide. The study supports previous research where it was seen that having higher concentrations of DHA in the red blood cell can reduce the risk of Alzheimer’s disease by 50 percent.
Fish oil contains EPA and DHA, two omega-3 fatty acids with a number of different functions in the brain and nervous system. It appears that middle-aged people who consume more oily fish or who take fish oil supplements have improvements in their brain structure and cognitive skills. This was shown in a study that is published in Neurology. The study results are quite interesting because cognitive decline and dementia are increasing problems that affect millions of people worldwide. The study supports previous research where it was seen that having higher concentrations of DHA in the red blood cell can reduce the risk of Alzheimer’s disease by 50 percent.
 Yes, according to a new study published in Free Radical Biology & Medicine, lack of
Yes, according to a new study published in Free Radical Biology & Medicine, lack of  According to a new study based on a number of systematic reviews and meta-analyses, the widespread lack of
According to a new study based on a number of systematic reviews and meta-analyses, the widespread lack of  Both physical traumas and critical illnesses are associated with inflammation and oxidative stress where free radicals can cause potentially life-threatening damage to cells and tissues. Traumas are estimated to be the cause of one in ten deaths. New research suggests that early intervention with
Both physical traumas and critical illnesses are associated with inflammation and oxidative stress where free radicals can cause potentially life-threatening damage to cells and tissues. Traumas are estimated to be the cause of one in ten deaths. New research suggests that early intervention with  All the different
All the different  Seniors have an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, which is the leading cause of death. It is commonly known that diet plays a key role in preventing these diseases, and a team of scientists therefore decided to look closer at
Seniors have an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, which is the leading cause of death. It is commonly known that diet plays a key role in preventing these diseases, and a team of scientists therefore decided to look closer at People suffering from the Crohn’s disease, an inflammatory bowel disorder, often lack
People suffering from the Crohn’s disease, an inflammatory bowel disorder, often lack